|
Here, we represent a facile strategy for the rational manipulation of green and red upconversion emission, and the pure dark red emission (650-670nm) of NaYF4: Yb/Er UCNPs has been achieved by manganese ions (Mn2+) doping. The existence of Mn2+ ions disturbs the transition possibilities between green and red emissions of Er3+ and facilitates the occurrence of red emission, resulting in an emission color output from green to red by rational controlling the Mn2+-doping level. Moreover, the Mn2+-doping also influences the growth dynamics to give simultaneous control of crystalline phase and size of the resulting UCNPs. By coating a PEG phospholipid layer on the surface of the NPs, the as-prepared UCNPs ware rendered water-soluble and then employed as luminescent probes for in vivo imaging. In addition, these PEGlyated UCNPs could also be employed as drug delivery carriers. A commonly used chemotherapeutic drug, doxorubicin (DOX), was loaded on these PEGylated UCNPs by physical adsorption through simple mixing. The release of DOX from UCNPs can be controlled by varying pH values, facilitating its drug delivery and controlled release to cancer cells. As a result, the as-prepared UCNPs with efficient red upconversion luminescence and drug delivery capabilities could be potentially employed as a platform for simultaneous in vivo bioimaging and therapeutic applications.
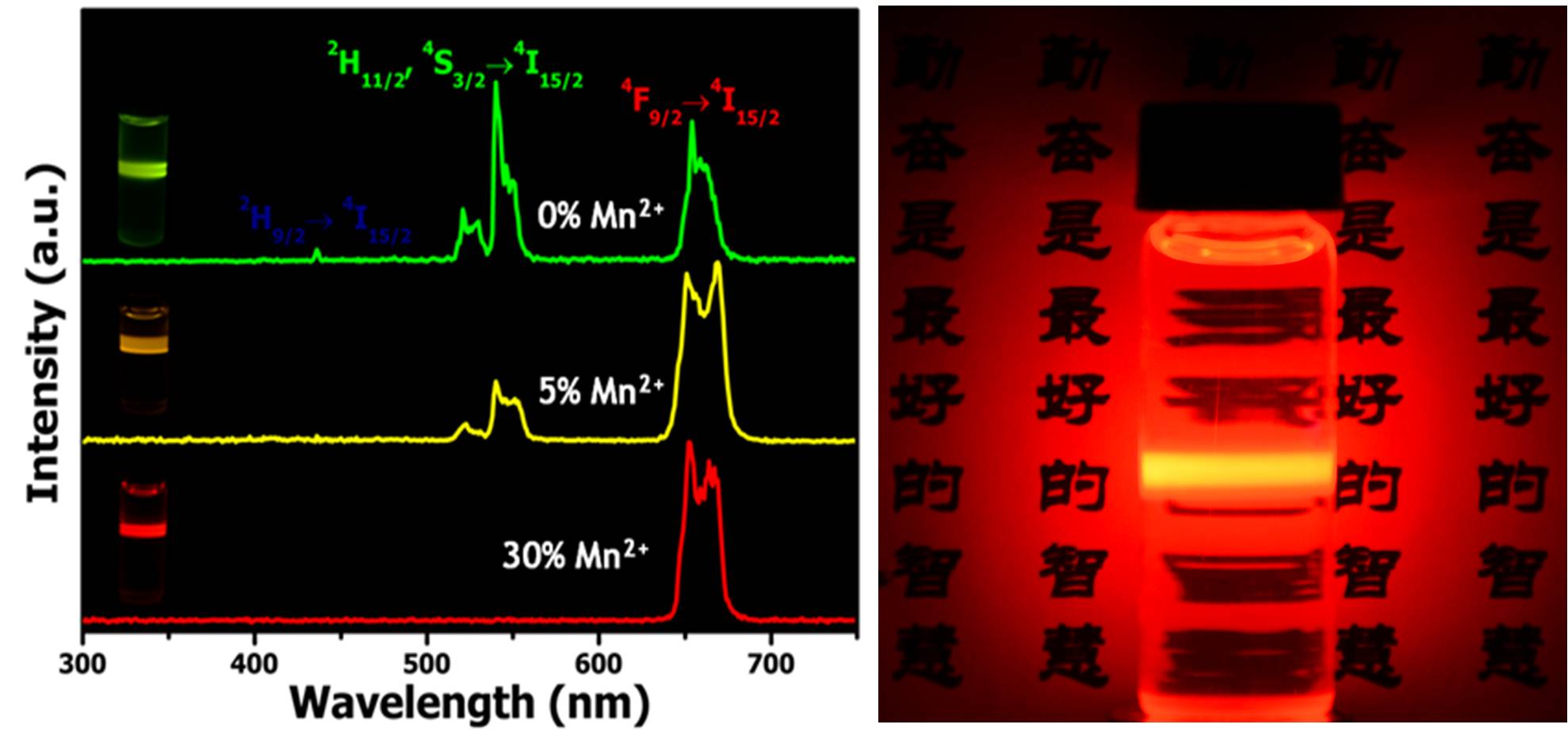
This research has been online published in Adv. Mater. (Gan Tian, Zhanjun Gu, Liangjun Zhou, Wenyan Yin, Xiaoxiao Liu, Liang Yan, Shan Jin, Wenlu Ren, Gengmei Xing, Shoujian Li, and Yuliang Zhao. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1226–1231).
This work was supported by National Basic Research Programs of China (973 program, No. 2012CB932504 and 2011CB933403), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21001108 and 21177128).
|

